Physiotherapy in Sarnia for Foot
Welcome to Sport And Spine Physiotherapy's patient resource about from foot injuries and surgery. The following is an article on foot anatomy. Please see the left hand menu for specific information on ankle injuries.
Our feet are constantly under stress. It's no wonder that 80 percent of us will have some sort of problem with our feet at some time or another. Many things affect the condition of our feet: activity level, occupation, other health conditions, and perhaps most importantly, shoes. Many of the problems that arise in the foot are directly related to shoes, so it is very important to choose shoes that are good for your feet.
The foot is an incredibly complex mechanism. This introduction to the anatomy of the foot will not be exhaustive but rather highlight the structures that relate to conditions and surgical procedures of the foot.
This guide will help you understand:
- what parts make up the foot
- how the foot works
#testimonialslist|kind:all|display:slider|orderby:type|filter_utags_names:Foot therapy|limit:15|heading:Hear from some of our *Foot Therapy* patients#
The important structures of the foot can be divided into several categories. These include:
- bones and joints
- ligaments and tendons
- muscles
- nerves
- blood vessels
Bones and Joints
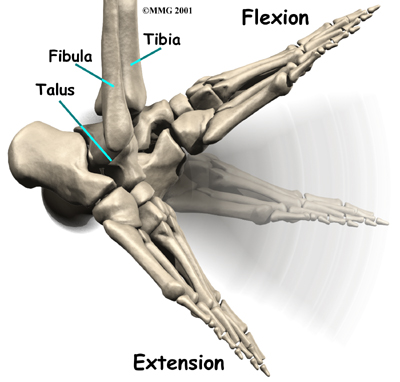
The skeleton of the foot begins with the talus, or ankle bone, that forms part of the ankle joint. The two bones of the lower leg, the large tibia and the smaller fibula, come together at the ankle joint to form a very stable structure known as a
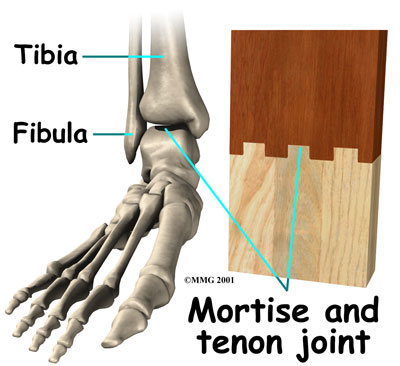
The mortise and tenon structure is well known to carpenters and craftsmen who use this joint in the construction of everything from furniture to large buildings. The arrangement is very stable.
The two bones that make up the back part of the foot (sometimes referred to as the ) are the talus and the calcaneus, or heelbone. The talus is connected to the calcaneus at the subtalar joint.
Foot Anatomy Bones & Joints
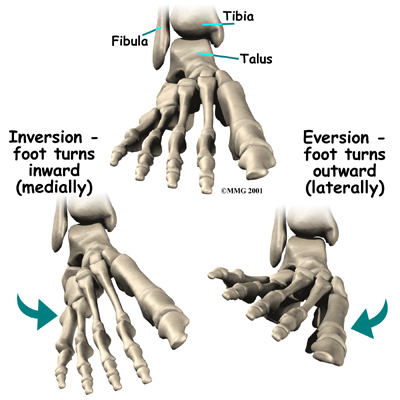
The ankle joint allows the foot to . The subtalar joint allows the foot to rock from .
Just down the foot from the ankle is a set of five bones called tarsal bones that work together as a group. These bones are unique in the way they fit together. There are multiple joints between the tarsal bones. When the foot is twisted in one direction by the muscles of the foot and leg, these bones lock together and form a very rigid structure. When they are twisted in the opposite direction, they become unlocked and allow the foot to conform to whatever surface the foot is contacting.
The tarsal bones are connected to the five long bones of the foot called the metatarsals. The two groups of bones are fairly rigidly connected, without much movement at the joints.

Finally, there are the bones of the toes, the phalanges. The joints between the metatarsals and the first phalanx is called the metatarsophalangeal joint (MTP). These joints form the ball of the foot, and movement in these joints is very important for a normal walking pattern.
Not much motion occurs at the joints between the bones of the toes. The big toe, or hallux, is the most important toe for walking, and the first MTP joint is a common area for problems in the foot.
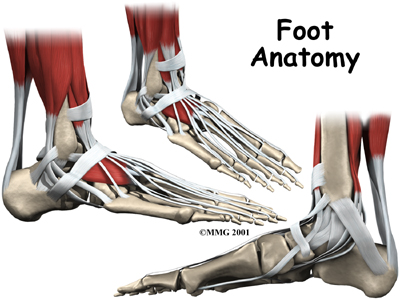
Ligaments and Tendons
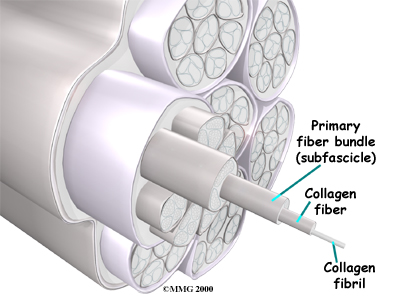
Ligaments are the soft tissues that attach bones to bones. Ligaments are very similar to tendons. The difference is that tendons attach muscles to bones. Both of these structures are made up of small fibers of a material called . The collagen fibers are bundled together to form a rope-like structure. Ligaments and tendons come in many different sizes, and like rope, are made up of many smaller fibers. The thicker the ligament (or tendon) the stronger the ligament (or tendon) is.
Foot Anatomy Ligaments & Tendons
The large is the most important tendon for walking, running, and jumping. It attaches the calf muscles to the heel bone to allow us to raise up on our toes. The posterior tibial 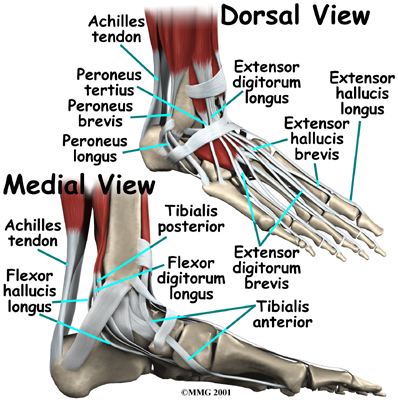 tendon attaches one of the smaller muscles of the calf to the underside of the foot. This tendon helps support the arch and allows us to turn the foot inward. The toes have tendons attached that bend the toes down (on the bottom of the toes) and straighten the toes (on the top of the toes). The anterior tibial tendon allows us to raise the foot. Two tendons run behind the outer bump of the ankle (called the lateral malleolus) and help turn the foot outward.
tendon attaches one of the smaller muscles of the calf to the underside of the foot. This tendon helps support the arch and allows us to turn the foot inward. The toes have tendons attached that bend the toes down (on the bottom of the toes) and straighten the toes (on the top of the toes). The anterior tibial tendon allows us to raise the foot. Two tendons run behind the outer bump of the ankle (called the lateral malleolus) and help turn the foot outward.
Many small ligaments hold the bones of the foot together. Most of these ligaments form part of the joint capsule around each of the joints of the foot. A joint capsule is a watertight sac that forms around all joints. It is made up of the ligaments around the joint and the soft tissues between the ligaments that fill in the gaps and form the sac.
Muscles
Most of the motion of the foot is caused by the stronger muscles in the lower leg whose tendons connect in the foot. Contraction of the muscles in the leg is the main way that we move our feet to stand, walk, run, and jump.
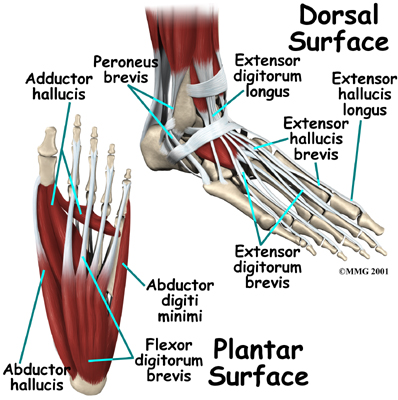
There are numerous small muscles in the foot. While these muscles are not nearly as important as the small muscles in the hand, they do affect the way that the toes work. Damage to some of these muscles can cause problems.
Most of the are arranged in layers on the sole of the foot (the plantar surface). There they connect to and move the toes as well as provide padding underneath the sole of the foot.
Nerves
The main nerve to the foot, the , enters the sole of the foot by running behind the inside bump on the ankle, the medial malleolus.
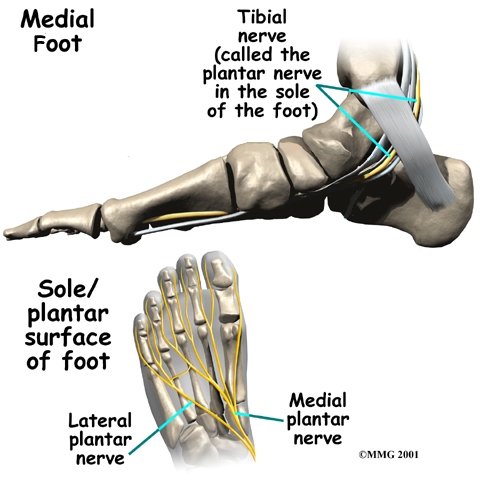
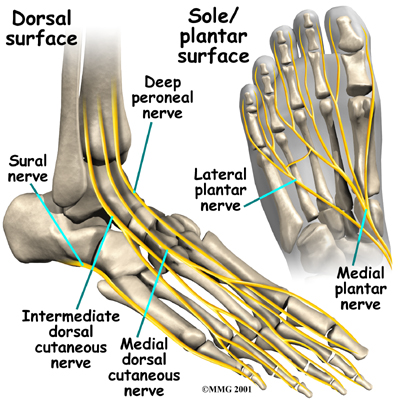
This nerve supplies sensation to the toes and sole of the foot and controls the muscles of the sole of the foot. Several run into the foot on the outside of the foot and down the top of the foot. These nerves primarily provide sensation to different areas on the top and outside edge of the foot.
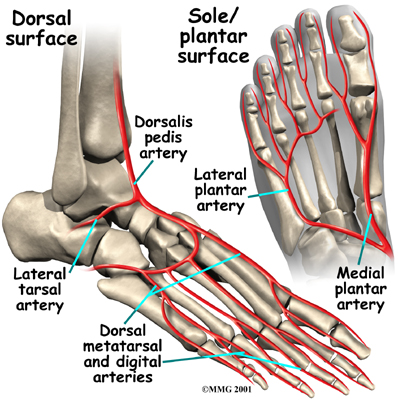
Blood Vessels
The main blood supply to the foot, the , runs right beside the nerve of the same name. Other less important arteries enter the foot from other directions.
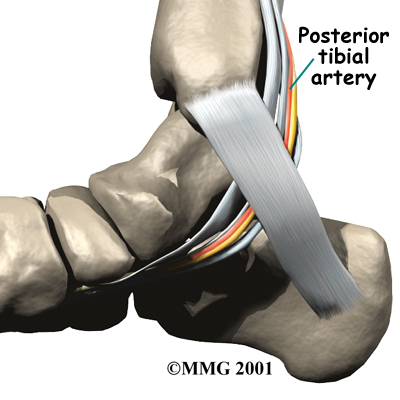
One of these arteries is the that runs down the top of the foot. You can feel your pulse where this artery runs in the middle of the top of the foot.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.


















 tendon attaches one of the smaller muscles of the calf to the underside of the foot. This tendon helps support the arch and allows us to turn the foot inward. The toes have tendons attached that bend the toes down (on the bottom of the toes) and straighten the toes (on the top of the toes). The anterior tibial tendon allows us to raise the foot. Two tendons run behind the outer bump of the ankle (called the lateral malleolus) and help turn the foot outward.
tendon attaches one of the smaller muscles of the calf to the underside of the foot. This tendon helps support the arch and allows us to turn the foot inward. The toes have tendons attached that bend the toes down (on the bottom of the toes) and straighten the toes (on the top of the toes). The anterior tibial tendon allows us to raise the foot. Two tendons run behind the outer bump of the ankle (called the lateral malleolus) and help turn the foot outward.








